Servo motors are motors that have been specifically created for use in robotics and control applications. They are utilised for highly pre...
Servo motors are motors that have been specifically created for use in robotics and control applications. They are utilised for highly precise position and speed control. It is made up of an appropriate motor, a position sensor, and an advanced controller. According to the motor that is controlled by the servomechanism, a servo motor can be classified as either a DC servo motor or an AC servo motor.
Therefore, the two main categories of servo motors are
- DC Servo motors and
- AC Servo motors.
How Does A Servo Motor Work?
Servo motors are used to precisely regulate position and speed, however in a straightforward scenario, simply position may be managed. A potentiometer that is connected to the motor shaft by gears may sense the mechanical position of the shaft. The potentiometer converts the shaft's current position into an electrical signal, which is then compared to the command input signal. Electronic encoders or sensors are utilised in contemporary servo motors to detect the position of the shaft.
According to the desired position of the shaft, command input is delivered. An error signal is produced if the feedback signal deviates from the input. The motor then rotates as a result of the erroneous signal being amplified and applied as input. Additionally, the motor remains stationary while holding the position when the shaft reaches the desired position and the error signal changes to zero.
Electrical pulses are used as the input for the commands. The speed of the motor is proportional to the difference between the current position and the needed position because the actual input provided to the motor is the difference between the feedback signal (current position) and applied signal (required position). The motor's power requirements are inversely correlated with the distance it must cover.

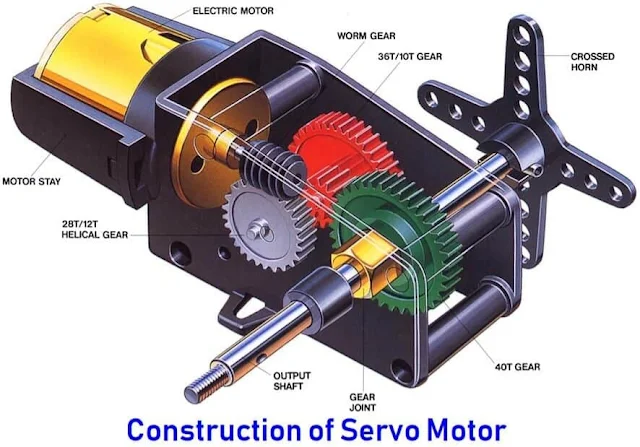





No comments